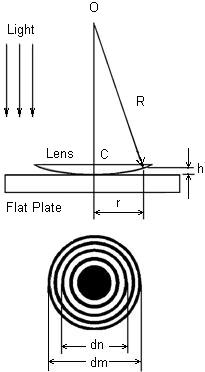
Schematic of a lens and a flat plate used to form Newton’s rings
Note: the actual power supply for Sodium lamp may look different
Features
Including Sodium lamp with power supply
Including reading microscope for accurate measurement
Compact structure
Detailed instruction manual
Introduction
The LEOK-30 Newton's Ring Experiment Apparatus is designed to demonstrate the optical phenomenon known as Newton's Rings, a classic interference pattern observed when light reflects between two surfaces—one spherical and one flat. The phenomenon was first studied by Isaac Newton and is an example of equal-thickness interference.
When viewed under monochromatic light, the interference results in concentric rings of alternating bright and dark bands. These rings are centered at the point of contact between the spherical and flat surfaces. This setup is an ideal educational tool for understanding interference, optical fringes, and thin film optics.
Key Features:
Visualization of Newton's Rings: The apparatus allows for the clear observation of the interference pattern formed by light reflecting between a spherical and flat surface.
Precision Measurement: The apparatus is designed to measure the spacing of interference fringes, which can then be used to calculate the radius of curvature of the spherical surface.
Educational Value: This kit provides valuable insight into the principles of interference and the properties of light waves.
The instruction manual contains comprehensive materials including experimental configurations, principles and step-by-step instructions. Please click to view some sample pages of the instruction manual.
Specifications
| Description | Specifications |
| Minimum Division of Reading Drum | 0.01 mm |
| Magnification | 20x, (1x, f = 38 mm for Objective; 20x, f = 16.6 mm for Eyepiece) |
| Working Distance | 76 mm |
| View Field | 10 mm |
| Measurement Range of Reticle | 8 mm |
| Measurement Accuracy | 0.01 mm |
| Sodium Lamp | 15 ± 5 V AC, 20 W |
| Radius of Curvature of Newton's Ring | 868.5 mm |
| Beam Splitter | 5:5 |
Part List
| Description | Qty |
| Sodium lamp with housing and power supply | 1 set |
| Reading microscope | 1 |
| Newton's ring assembly (SZ-37B) | 1 |
| Beam splitter | 1 |
| Focusing knob | 1 |

Schematic of a lens and a flat plate used to form Newton’s rings